区块链(BlockChain)
Block Chain (Block Chain)
定义:区块链是一个共享的、不可变的分类帐,用于记录交易、跟踪资产和建立信任。本质上是一个去中心化的分布式账本数据库,其本身是一串使用密码学相关联产生的数据块,每一个数据块上包含了多次比特币网络交易有效的确认信息。
Definition: The block chain is a shared, variable ledger for recording transactions, tracking assets and building trust. In essence, it is a decentralised distributed account database, which itself is a series of data blocks generated by cryptography, each containing valid confirmation information for multiple Bitcoin network transactions.
共享的理解:它要求我们所有的人共用同一本账本。所有的参与方从原材料的第一步一直到最终的使用者、消费者、买单者每个人都可以去查看账本。它是全透明的、有距离的、不可修改的、不可删除的。
Shared understanding: It requires all of us to share the same account book. Each participant can go from the first step of the raw material to the end user, consumer, buyer. It is transparent, remote, unalterable and undeletable.
现在网上购物的时候,如果说除了整个快递和支付的过程,自己也可以跟踪,对于商品的起源、生产的源头都可以追溯的话,那么就可以解决消费时候的疑虑。有一些乳制品企业现在已经在做这方面的尝试了,这是从消费者的角度
Now, when we're shopping online, if we can track the whole delivery and payment process by ourselves, and if we can trace the origin of the goods and the origin of the production, then we can solve the concerns about the consumption. Some dairy companies are now trying to do this, from the consumer's point of view.
不可变的理解:不能随意更改数据。例如商品的例子。hash算法,给任意一个文件生成了一串固定长度的乱码一样的标签,算法是不可逆的,就是说,你拿到这个标签,无法反向推导出原来的数据文件。正是这种不可逆性,决定了区块链的不可更改性。每个区块中,除了十分钟内的转账交易数据之外,还有一个区块头。区块头包含了对上一个区块数据的 hash 值。这些 hash 层层嵌套,长度固定,最终将所有区块串联起来,形成区块链
Irreversible understanding: Data cannot be changed at will. Examples of commodities, for example. Hash algorithms, which produce a series of random labels of fixed lengths for any one file, are irreversible, meaning that you have this label and cannot invert the original data files. It is this irreversibility that determines the non-changeability of the block chain. In each block, in addition to the transfer transaction data within 10 minutes, there is a block. The block head contains the hash value of the data of the previous block. These hash layers are embedded, fixed in length, and eventually all blocks are bound together to form a block chain.
去中心化的理解:
Let's get to the bottom of this:
中心化与去中心化的对比(谁拥有记账权)
Centralization versus decentralization (who has rights to account)
1.中心化机构拥有公认”记账权”
1. Centralized institutions have recognized “account rights”

2.去中心化的区块链网络所有人具有”记账权”
The owner of the decentralised block chain network has the “right to account”

区块链是什么的例子:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1J7411Z7T9?from=search&seid=5524688675302547308
What is the example of the block chain:
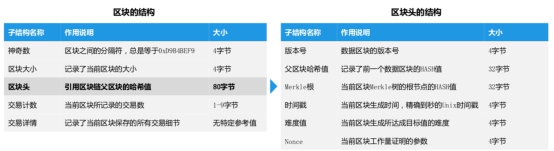
区块链的结构:
Structure of the block chain:
一个完整区块是由神奇数、区块大小、数据区块头部信息、交易计数、交易详情等组成。在这当中,数据区块头部信息的HASH值是下一个新区 块的HASH值的参考目标数,最后一项交易详情记录了该区块中所有的交易记录。
A complete block consists of magic numbers, block size, data block head information, transaction counts, transaction details, etc. In this case, the HSH value of the data block head information is the reference number for the HSH value of the next new block, and the last transaction details record all transactions in the block.
区块头由4字节的版本号、32字节的上一个区块的散列值、32字节的Merkle Root Hash、4字节的时间缀、4字节的当前难度值、4字节的随机数 组成。区块包含的交易列表则附加在区块头后面,其中的第一笔交易是coinbase交易,这是一笔为了让矿工获得奖励及手续费的特殊交易。 见图示:
The block header consists of a version number of four bytes, a hash value of the previous 32 bytes, a 32 byte Merkel Root Hash, a 4 byte suffix, a 4 byte current difficulty value, and a 4 byte random number. The block contains a list of transactions that are attached to the block head, the first of which is a coinbase transaction, which is a special transaction to give miners incentives and fees.

链式结构
Chain structure
矿工挖矿的过程 就是产生新的数据区块的过程,这个过程需要对比前一个数据区块头部的HASH值和随机数,如
The process of mining by miners is the process of generating new data blocks that require comparison of HSH values and random numbers on the head of the previous data block, such as:
注册有任何问题请添加 微信:MVIP619 拉你进入群

打开微信扫一扫
添加客服
进入交流群

















发表评论