舍勒发现氯气是在1774年,当时他正在研究软锰矿(二氧化锰),当他使软锰矿与浓盐酸混合并加热时,产生了一种黄绿色的气体,这种气体的强烈的刺激性气味使舍勒感到极为难受,但是当他确信自己制得了一种新气体后,他又感到一种由衷的快乐。
Sheller discovered that chlorine gas was in 1774, when he was studying soft manganese (manganese dioxide) and when he mixed and heated the soft manganese with concentrated hydrochloric acid, he produced a yellow green gas, whose strong irritant odor made Sheller very uncomfortable, but when he was convinced that he had produced a new gas, he was sincerely happy.
舍勒制备出氯气以后,把它溶解在水里,发现这种水溶液对纸张、蔬菜和花都具有永久性的漂白作用;他还发现氯气能与金属或金属氧化物发生化学反应。从1774年舍勒发现氯气以后,到1810年,许多科学家先后对这种气体的性质进行了研究。这期间,氯气一直被当作一种化合物。直到1810年,戴维经过大量实验研究,才确认这种气体是由一种化学元素组成的物质。他将这种元素命名为chlorine,这个名称来自希腊文,有“绿色的”意思。我国早年的译文将其译作“绿气”,后改为氯气。
When the chlorine gas was prepared by Sheller, it dissolved in water and found that the water solution had a permanent bleaching effect on paper, vegetables and flowers; he also found that the chlorine gas was chemically reacting to metals or metal oxides. After the chlorine gas was discovered in Sheller in 1774, many scientists studied the nature of the gas in 1810. The chlorine gas was treated as a compound during this period. It was only in 1810 that David, after extensive experimental research, confirmed that the gas was a chemical element. He named the element as chlorine, a Greek term that meant “green”. We translated it into “green gas” and then converted it into chlorine gas.
氯气的生产方法经历了漫长的发展过程。1774年瑞典化学家舍勒用软锰矿(含有二氧化锰)和浓盐酸作用,首先制得了氯气,其反应方程式为:
The method of production of chlorine gas has been developed over a long period of time. In 1774, Swedish chemist Scheller used soft manganese mines (containing manganese dioxide) and concentrated hydrochloric acid to first produce chlorine gas, with a response equation of:
4HCl(浓)+MnO?=加热=MnCl?+2H?O+Cl?↑
4HCl + MNO? = Heated = MnCl?+2H?O+Cl?
然而,由于当时还不能够大量制得盐酸,故这种方法只限于实验室内制取氯气。后来法国化学家贝托雷把氯化钠、软锰矿和浓硫酸的混合物装入铅蒸馏器中,经过加热制得了氯气,其反应方程式为:
However, since it was not possible to produce a large amount of hydrochloric acid at that time, this method was limited to producing chlorine gas in the laboratory. The French chemist Betore later loaded the mixture of sodium chloride, soft manganese ore and sulfuric acid into lead distillers, which were heated to produce chlorine gas, with a response equation of:
2NaCl+3H?SO?(浓)+MnO?=加热=2NaHSO?+MnSO?+2H?O+Cl?↑
2 NaCl+3H? SO? (Short) + MNO? = Heated = 2 nso? + MnSO? + 2H? O+Cl?
因为此法原料易得,所以,自1774年舍勒制得氯气到1836年止,人们一直沿用贝托雷发明的方法来生产氯气。
Because of the ease with which this material is available, chlorine gas has been produced from Shearer in 1774 until 1836, following the methods invented by Betore.
1836年古萨格发明了一种焦化塔,用来吸收路布蓝法生产纯碱(Na?CO?)的过程中排出的氯化氢气体(以前这种含氯化氢的气体被认为是一种废气,从古萨格开始,才得到了充分利用)得到盐酸,从此盐酸才成为一种比较便宜的酸,可以广为利用.舍勒发明的生产氯气的方法,经过改进,到此时才成为大规模生产氯气的方法。
In 1836, the Goussag invented a pyrochloric tower to absorb the hydrogen chloride gas emitted during the production of pure alkalis (Na?CO?) in the Lybuland process (the former hydrogen chloride gas was considered to be a waste gas and was fully exploited from Gossag), from which the hydrochloric acid became a cheaper acid that could be used widely for the production of chlorine gas by. Sheller, which was improved to become a method for large-scale production of chlorine gas.
1868年狄肯和洪特发明了用氯化铜作催化剂,在加热时,用空气中的氧气来氧化氯化氢气体制取氯气的方法,其反应方程式为:
In 1868, Deacon and Hundt invented the use of copper as a catalyst to extract chlorine from the air oxygen oxide system when heated, with the following response equations:
4HCl+O?=2H?O+2Cl?↑
这种方法被称为狄肯法。(又译为地康法)
It's called Dickenlaw.
上面这些生产氯气的方法,虽然在历史上都起过一定的作用,但是它们与电解法生产氯气相比,无论从经济效益还是从生产规模上,都大为逊色.当电解法在生产上付诸实用时,上述生产氯气的方法就逐渐被淘汰了。
The above methods of production of chlorine gas, although historically useful, are much worse than those of electrolytic production of chlorine, both economically and on the scale of production... When electrolytic methods are applied to production, the methods of production of chlorine gas are gradually phased out.
电解法的诞生要追溯到1833年。法拉第经过一系列的实验,发现当把电流作用在氯化钠的水溶液时,能够获得氯气,其反应方程式为:
The electrolytic process dates back to 1833. Faraday, after a series of experiments, found that when the current works in the water solution of sodium chloride, chlorine gas can be obtained and its response equation is as follows:
2NaCl+2H?O==2NaOH+H?↑+Cl?↑
后来,英国科学家瓦特也发现了这种方法,并在1851年获得了一份关于生产氯气的英国专利。但是由于当时没有实用的直流发电机以产生足够的电流,所以电解法也只能停留在实验室规模,不能付诸工业生产,而被束之高阁。一直到十九世纪七十至八十年代,出现了比较好的直流发电机,电解法才得到广泛的应用。从此,氯气的工业生产跨入了一个新纪元。然而当时电解制取氯气所使用的电极为汞,致使电解得到的氯气、氢气中混有相当多的汞蒸气。这种“汞法制氯”对环境危害很大,所以新的“离子交换膜法”制取氯气,更环保,更节能。(汞法制氯是制取氯气的主流方法,如2010年中国有46%的氯气,2000年西欧50.1%的氯气都为此法生产的)。
The method was later discovered by British scientist Walter, who obtained a British patent for the production of chlorine gas in 1851. However, since there was no functional direct-flow generator to generate sufficient currents, the electrolysis method was confined to laboratory size and could not be used for industrial production. Until the 1970’s and 1980’s, a better direct-flow generator became available, and the electrolytic method was widely applied. Industrial production of chlorine gas has since entered a new era. However, the electrolytic use of chlorine gas had resulted in a significant amount of mercury vapour mixed with the electrolysis chlorine gas and hydrogen gas. The new “ionic exchange membranes” used to extract chlorine from the environment, making it more environmentally friendly and energy-efficient. (The mercury legal chlorine is the dominant method for the extraction of chlorine gas, as in China there were 46% of chlorine in 2010 and 50.1% of chlorine from Western Europe in 2000.)
物质结构
Physical Structure
原子结构:氯原子最外层有7个电子,反应中易得到1个电子或共用一个电子对达到稳定结构(共价键)。
Atom structure: The outer outermost layer of chlorine has seven electrons, with a response that makes it easier to obtain one electron or to share one electron pair to reach a stable structure (combined price keys).
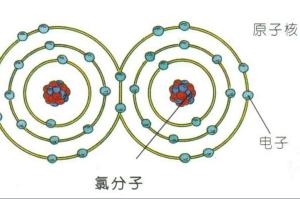 分子结构图分子结构:氯分子为双原子分子,分子式Cl?。
分子结构图分子结构:氯分子为双原子分子,分子式Cl?。
状态
Status
常温常压下为有强烈刺激性气味的黄绿色的气体。
The constant heat pressure is a yellow green gas with a strong irritant odor.
密度
Density
氯气密度是空气密度的2.5倍,标况下ρ=3.21kg/m3。
The chlorine gas density is 2.5 times the air density, as it is constant = 3.21 kg/m3.
易液化
Liquefied
熔沸点较低,常温常压下,熔点为-101.00℃,沸点-34.05℃,常温下把氯气加压至600~700kPa或在常压下冷却到-34℃都可以使其变成液氯,液氯是一种油状的液体,其与氯气物理性质不同,但化学性质基本相同。
The lower boiling point, the constant temperature pressure, the melting point -101.00°C, the boiling point -34.05°C, and the constant temperature pressure of the chlorine gas to 600-700 kPa or cooling to 34°C can transform it into liquid chlorine, which is an oily liquid that differs from the physical properties of the chlorine gas but is essentially the same chemical properties.
溶解性
Solubility
可溶于水,易溶于有机溶剂(例如:四氯化碳)难溶于饱和食盐水。1体积水在常温下可溶解2体积氯气,形成黄绿色氯水,密度为 3.170g/L,比空气密度大。
Soluble in water, soluble in organic solvents (e.g. carbon tetrachloride) is indissoluble in saturated salt water. 1 Volume water solubles 2 volume chlorine gas at constant temperatures, resulting in yellow green chlorine water with a density of 3.170 g/L, which is larger than air density.
自然分布
Natural distribution
自然界中游离状态的氯存在于大气层中,不过此时的氯气受紫外线经常会分解成两个氯原子(自由基)。是破坏臭氧层的主要单质之一。
Fluid chlorine in nature is present in the atmosphere, but at this time chlorine is often decomposed into two chlorine atoms (freeze bases) by ultraviolet light. It is one of the main monolithics that destroy the ozone layer.
助燃性
Fugitive
氯气支持燃烧,许多物质都可在氯气中燃烧(除少数物质如碳单质等)。
Chlorine gas supports combustion and many substances can be burned in chlorine gas (with the exception of a few substances such as carbon monomer).
与金属反应
Reactions with Metals
1、与钠的反应:2Na+Cl2=2NaCl
1. Reactions with sodium: 2Na+Cl2=2NaCl
 钠在氯气中燃烧现象:钠在氯气里剧烈燃烧,产生大量的白烟,放热。
钠在氯气中燃烧现象:钠在氯气里剧烈燃烧,产生大量的白烟,放热。
2、与铜的反应:Cu+Cl2=CuCl2
Reactions with copper: Cu+Cl2=CuCl2
 铜在氯气中燃烧现象:红热的铜丝在氯气里剧烈燃烧,瓶里充满棕黄色的烟,加少量水后,溶液呈蓝绿色(绿色较明显),加足量水后,溶液完全显蓝色。
铜在氯气中燃烧现象:红热的铜丝在氯气里剧烈燃烧,瓶里充满棕黄色的烟,加少量水后,溶液呈蓝绿色(绿色较明显),加足量水后,溶液完全显蓝色。
3、与铁的反应:2Fe+3Cl2=2FeCl3
3. Response with iron: 2Fe+3Cl2=2FeCl3
 铁在氯气中燃烧现象;铁丝在氯气里剧烈燃烧,瓶里充满棕红色烟,加少量水后,溶液呈黄色。
铁在氯气中燃烧现象;铁丝在氯气里剧烈燃烧,瓶里充满棕红色烟,加少量水后,溶液呈黄色。
4、与镁的反应:Mg+Cl2=MgCl2
4. Reactions to magnesium: Mg+Cl2=MgCl2
 镁在氯气中燃烧现象;非常剧烈的燃烧,生成白色的烟。
镁在氯气中燃烧现象;非常剧烈的燃烧,生成白色的烟。
注:氯气具有强氧化性,加热下可以与所有金属反应,如金、铂在热氯气中燃烧,而与Fe、Cu等变价金属反应则生成高价金属氯化物。
NOTE: Chlorine gas is highly oxidizing and can react with all metals, e.g. gold, platinum burning in thermal chlorine gas, while reaction with variable metals such as Fe, Cu produces high-value metal chlorides.
常温下,干燥氯气或液氯不与铁反应,只能在加热情况下反应,所以可用钢瓶储存氯气(液氯)。
At constant temperatures, dry chlorine gas or liquid chlorine does not react with iron and can only react with heating, so a bottle can be used to store chlorine gas (liquid chlorine).
与非金属反应
Reactions with non-metal
1、与氢气的反应:H?+Cl?=点燃=2HCl
1. Reactions with hydrogen gas: H?+Cl?=Firing = 2HCl
 氯气与氢气反应现象:H?在Cl?中安静地燃烧,发出苍白色火焰,瓶口处出现白雾。
氯气与氢气反应现象:H?在Cl?中安静地燃烧,发出苍白色火焰,瓶口处出现白雾。
H?+Cl?=光照=2HCl
H? +Cl?
现象:H?在Cl?中安静地燃烧,发出苍白色火焰,瓶口处出现白雾。
Symptoms: H? Quietly burning in Cl?.....................................................................................................................................................
注:将点燃的氢气放入氯气中,氢气只在管口与少量的氯气接触,产生少量的热;点燃氢气与氯气的混合气体时,大量氢气与氯气接触,迅速化合放出大量热,使气体急剧膨胀而发生爆炸。工业上制盐酸使氯气在氢气中燃烧。氢气在氯气中爆炸极限是9.8%~52.8%。
Note: Fired hydrogen gas is placed in chlorine gas, which is exposed only to a small amount of chlorine gas at the tube mouth, producing a small amount of heat; when the mixture of hydrogen gas and chlorine gas is ignited, large quantities of hydrogen gas is exposed to chlorine gas, which quickly melts out a large amount of heat, causing the gas to swell and explodes. Industrial hydrochloric acid burns chlorine in hydrogen gas. Hydrogen explosion limits in chlorine are 9.8 - 52.8 per cent.
 磷在氯气中燃烧2、与磷的反应:2P+3Cl?(少量)=点燃=2PCl?
磷在氯气中燃烧2、与磷的反应:2P+3Cl?(少量)=点燃=2PCl?
2; reactions with phosphorus:2P+3Cl? (small) =2PCl?
2P+5Cl?(过量)=点燃=2PCl5
2P+5Cl?(overdose) = ignition = 2PCl5
现象:产生白色烟雾
Symptoms: generation of white smoke
3、与硫的反应:2S+Cl?=点燃=S?Cl?
3. Reactions to sulphur: 2S+Cl?=Firing = S?Cl?
注:在一定条件下,氯气还可与S、Si等非金属直接化合。
NOTE: Chlorine gas can also be directly assimilated to non-metals such as S, S etc. under certain conditions.
4、与水反应:Cl?+H?O=HCl+HClO(可逆反应)
4. Reaction with water: Cl?+H?O=HCl+HCLO (reversible)
现象:水变黄绿色,气泡在水里又冒出来,有刺激性气味。
Symptoms: The water turns yellow and green, bubbles resurface in the water, and it smells irritant.
注:在该反应中,氧化剂是Cl?,还原剂也是Cl?,本反应是歧化反应。氯气遇水会产生次氯酸,次氯酸具有净化(漂白)作用,用于消毒——溶于水生成的HClO具有强氧化性。
NOTE: In this reaction, the oxidizer is Cl?, the reduction agent is also Cl?, and the reaction is discriminatory. Chlorine gas in water produces hypochloric acid and hypochloric acids are purified (white) for disinfection - HCLO soluble in water is highly oxidizing.
5、与二氧化硫和水反应:SO?+Cl?+2H?O=H?SO?+2HCl
5. Reaction with sulphur dioxide and water: SO?+Cl?+2H?O=H?SO?+2HCl
6、与碱溶液反应:Cl2+2NaOH=NaCl+NaClO+H2O
6. Reaction with alkaline solution: Cl2+2NaOH=NaCl+NaClo+H2O
2Cl2+2Ca(OH)2=CaCl?+Ca(ClO)2+2H2O
注:上述两反应中,Cl?作氧化剂和还原剂,是歧化反应。
Note: In both of the above reactions, Cl. as oxidizers and reduction agents are discriminatory reactions.
7、与盐溶液反应: Cl2+2FeCl2=2FeCl3
7. Reaction with salt solution: Cl2+2 FeCl2=2FeCl3
Cl2+Na2S=2NaCl+S
Cl2+2I-=2Cl-+I2↓
Cl2+2Br-=2Cl-+Br2↓
注:中学阶段用来证明氯气非金属性和氧化性比硫强。
Note: The secondary school level is used to demonstrate that chlorine gas is not metal and oxidized more than sulphur.
8、与二硫化碳反应:CS2+3Cl2→CCl4+S2Cl2
8. Response with carbon dioxide: CS2+3Cl2CCl4+S2Cl2
注:反应条件为90℃到100℃。
Note: Reaction conditions are 90°C to 100°C.
9、与甲烷的反应:CH?+Cl?—光照→CH?Cl+HCl
9. Reactions to methane: CH?+Cl?—Light ~ CH?Cl+HCl
CH?Cl+Cl?—光照→CH?Cl?+HCl
CH? Cl+Cl?
CH?Cl?+Cl?—光照→CHCl?+HCl
♪ CHL? ♪ +Cl? ♪ - ♪ Light ♪ CHCl? ♪ ♪ HCl?
CHCl?+Cl?—光照→CCl?+HCl
CHCl? +Cl? - Light. CCl? + HCl
现象:黄绿色气体消失,容器内壁出现液珠,容器内压强下降。氯气与甲烷反应时,四个反应同时进行。
Symptoms: Yellow green gas disappears, liquid beads appear on the inner walls of the packaging and pressure drops in the inner pressure of the packaging.
10、与乙烯的反应:CH?=CH?+Cl?→CH?ClCH?Cl(1,2-二氯乙烷)(加成反应)
10, Reactions with ethylene: CH?=CH?+Cl?§CH?ClCH?Cl(1,2-dichloroethane) (with reaction)
11、与苯的反应:C6H6+ 3Cl2→ C6H6Cl6
Reactions to benzene: C6H6+3Cl2C6H6Cl6
注:该取代反应在氯化铁的催化下才能发生。
Note: This replacement response can only occur with the catalytic effect of iron chloride.
CAS号:7782-50-5
CAS: 7782-50-5
MDL号:MFCD00010934
MDL: MFCD00010934
EINECS号:231-959-5
EINECS: 231-959-5
RTECS号:FO2100000
RTECS: FO21,000,000
BRN号:3902968
BRN: 3902968
PubChem号:暂无[1]
PubChem: not available [1]
1、摩尔折射率:11.74
1 Moor Refraction Rate: 11.74
2、摩尔体积(cm3/mol):51.3
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 51.3
3、等张比容(90.2K):109.0
3 Equivalent (90.2K): 109.0
4、表面张力(dyne/cm):20.4
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 20.4
5、介电常数:无可用的
5. Intermediary constant: not available
6、极化率(10-24cm3):4.65
6. Polarisation rate (10-24 cm3): 4.65
7、单一同位素质量:69.937705 Da
7. Single isotope mass: 69.937705 Da
8、标称质量:70 Da
Nominal Quality: 70 Da
9、平均质量:70.906 Da[1]
Average mass: 70.906 Da [1]
1.疏水参数计算参考值(XlogP):1.6
1. Dehydration parameter calculation reference value (XlogP): 1.6
2.氢键供体数量:0
Number of hydrogen key suppliers: 0
3.氢键受体数量:0
3. Number of hydrogen key receptors: 0
4.可旋转化学键数量:0
4. Number of rotationable chemical keys: 0
5.互变异构体数量:无
5. Number of mutated isomers: none
6.拓扑分子极性表面积0
6. Topo molecule polar surface area 0
7.重原子数量:2
7. Number of heavy atoms: 2
8.表面电荷:0
8. Surface charge: 0
9.复杂度:0
9. Complexity: 0
10.同位素原子数量:0
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11.确定原子立构中心数量:0
11. Determination of the number of atomic centres: 0
12.不确定原子立构中心数量:0
12. Undetermined number of atomic centres: 0
13.确定化学键立构中心数量:0
13. Number of chemical key formation centres determined: 0
14.不确定化学键立构中心数量:0
14. Undetermined number of chemical key construction centres: 0
15.共价键单元数量:1[1]
Number of co-pricing keys units: 1 [1]
危险运输编码:UN 1017 2.3
Hazardous transport code: UN 1017 2.3
危险品标志:有毒危害环境
Hazard signs: Toxic hazard to the environment
安全标识:S9S45S61
Security marking: S9S45S61
危险标识:R23R50R36/37/38[1]
Hazard identification: R23R50R36/37/38 [1]
1、工业生产中用直流电电解饱和食盐水法来制取氯气:
1. Direct current electrolytic saturation and salt water in industrial production to produce chlorine gas:
2NaCl+2H?O=通电=H?↑+Cl?↑+2NaOH
2 NaCl+2H?O=electric = H? Cl?2Naoh
 氯碱工业氯碱工业始于 20世纪 20年代,氯气的生产主要是采用电解卤水(饱和食盐水)。
氯碱工业氯碱工业始于 20世纪 20年代,氯气的生产主要是采用电解卤水(饱和食盐水)。
精制的饱和食盐水注入电解槽后,在直流电的作用下进行电解 ,其电极反应如下:
The fine saturated saturated water is injected into the electrolysis cell and electrolysis is performed as a result of direct current electricity. The electrodes react as follows:
阳极反应:2Cl-- 2e → Cl2↑
Anode: 2Cl -- 2eCl2
阴极反应:2H2O+ 2e → H2↑+ 2OH-
cathode reaction: 2H2O+2e H22OH-
总反应: 2NaCl+ 2H2O → 2NaOH+ Cl2↑+ H2↑
Total response: 2NCl+ 2H2O 2NaOH+Cl2H2
通过电解槽出来的氯气中含有许多杂质,如氢气、水蒸气、三氯化氮等 ,必须进行消除杂质或进行干燥处理。
The chlorine gas from electrolysis cells contains many impurities, such as hydrogen gas, water vapour and nitrogen trichloride, which must be eliminated or dried.
2、其它冶金工业的副产品,如冶镁:MgCl2(熔融)=电解=Mg + Cl2↑
2. By-products of other metallurgical industries, such as magnesium: MgCl2 (melting) = electrolysis = Mg + Cl2 zirconium
炼钠:2NaCl(熔融)=电解=2Na + Cl2↑
Sodium refined: 2 NaCl = electrolysis = 2 Na + Cl2 zirconium
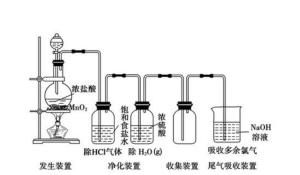 实验室制法实验室通常用氧化浓盐酸的方法来制取氯气:
实验室制法实验室通常用氧化浓盐酸的方法来制取氯气:
laborator
常见的氧化剂有:MnO?、KMnO?、Ca(ClO)?、Co2O3
Common oxidizers are MNO?, KMNO?, Ca(CLO)?, Co2O3.
发生的反应分别是:
The responses were as follows:
4HCl(浓)+MnO?=加热=MnCl?+Cl?↑+2H?O
4HCl + MNO? = Heated = MnCl? +Cl? 2H?O
16HCl+2KMnO?=2KCl+2MnCl?+8H?O+5Cl?↑
(这两个反应用的盐酸比较稀的话,反应将不再进行,没有盐酸可用一种非还原性酸和氯化钠的混合物代替,也可产生氯气。)
(If the hydrochloric acids used for these two reactions are rare, the reaction will no longer take place, and no hydrochloric acid can be replaced by a mixture of non-modified acids and sodium chloride, which can also generate chlorine gas.
4HCl+Ca(ClO)?=CaCl?+2H?O+2Cl?↑ (此反应需要的盐酸很稀,1mol/L便可以剧烈反应。)
4 HCl+Ca(CLO)?=CaCl?+2H?O+2Cl? (This response requires very thin hydrochloric acid, 1mol/L can react violently.
2H++ClO-+Cl-=H2O+Cl2↑
【只要能电离出H+的酸即可参加并且发生此归中反应;如:草酸。但由于参加反应的酸电离出的H+能力的不同,反应的速率也会不同。如果此酸为有机酸,且易挥发,那么要注意不能在强光照的照射下反应,不然氯气可能会和挥发出来的有机酸发生取代反应发生爆炸或生成有毒物质,如:冰醋酸会和氯气发生取代反应生成氯醋酸(剧毒固体)、二氯醋酸(固体)、三氯醋酸(固体)】
[Acids emitted from H+ can participate and react; e.g., acetic acid. The response rate can vary depending on the ability of the responding acid to emitted H+. If the acid is organic and volatilized, then care must be taken that it cannot react under high light exposure, otherwise chlorine gas may explode or produce toxic substances in lieu of the waved organic acid, e.g., ice acetic acid and chlorine gas will react in lieu of chloroacetic acid (very toxic solids), dichlorine acetic acid (solids), trichlorine acetic acid (solids)].
如不用浓盐酸,亦可用NaCl(固体)跟浓硫酸来代替。如:
NaCl (solid) and sulfuric acid can also be replaced if no concentrated hydrochloric acid is used. e.g.:
2NaCl+3H?SO?(浓)+MnO?=加热=2NaHSO?+MnSO?+2H?O+Cl?↑
2 NaCl+3H? SO? (Short) + MNO? = Heated = 2 nso? + MnSO? + 2H? O+Cl?
总之,实验室制氯气的办法都围绕着一个核心:氯离子+氧化剂+酸性环境,氧化剂的氧化性不强的话还需不同程度加热。
In summary, the laboratory chlorine approach revolves around one core: the chlor ion + oxidizer + acid environment, where the oxidizer is less oxidized and heated to varying degrees.
收集方法:用向上排空气法或者排饱和食盐水法
Collection method : Upward air drainage or saturated salt water
净化方法:用饱和食盐水出去HCl气体,用浓硫酸除去水蒸气。
Depuration method : release HCl gas with saturated salt water and remove water vapour from sulfuric acid.
尾气吸收:用强碱溶液(如NaOH溶液)吸收。
tail gas absorption : Absorption with strong alkaline solutions (e.g., NaOH solutions).
验满方法:⑴ 将湿润的淀粉-KI试纸靠近盛Cl2瓶口,观察到试纸立即变蓝,则证明已集满。
Filling method : (1) Filling of wet starch-KI test paper close to the mouth of the fine Cl2 bottle, as soon as it becomes blue.
⑵ 将湿润的蓝色石蕊试纸靠近盛Cl2瓶口,观察到试纸先变红后褪色,则证明已集满。
(2) The humid blue prune test paper closes to the entrance of the fine Cl2 bottle and the test paper is observed to be red and faded before it is shown to be full.
⑶ 实验室制备氯气时,常常根据氯气的颜色判断是否收集满。
(3) In laboratory preparation of chlorine gas, full collection is often judged by the colour of chlorine gas.
注意:切勿被网络上的无知言论欺骗,氯酸盐绝对不能用来制备氯气,因为会生成大量难以分离且易爆炸的ClO2。
Note: should not be deceived by the ignorance of the Internet, and chlorate should never be used to prepare chlorine gas because it will generate a large number of hard-to-separate and explosive CLO2.
据统计,20世纪90年代初期化学工业营业额的半数以上与氯有关;化学工业人员中有1/4左右从事与氯有关的活动。用于化学工业和医药工业的氯量约占其总产量的75%。1993年美国产量最大的50种化工产品中,氯的产量仅次于硫酸、氮气、氧气、乙烯、生石灰、氨气和氢氧化钠,居第8位。自从60年代以来,一个国家的氯产量常被看做是化学工业发展水平的重要标志。
According to statistics, more than half of the turnover of the chemical industry in the early 1990s was chlorine-related; about a quarter of the chemical industry was involved in chlorine-related activities. Chlorine used in the chemical and pharmaceutical industries accounted for about 75 per cent of its total production. Chlorine production in 1993 was second only to sulphuric acid, nitrogen gas, oxygen, ethylene, lime production, ammonia and sodium hydroxide.
化学工业用于生产次氯酸钠、三氯化铝、三氯化铁、漂白粉、溴素、三氯化磷等无机化工产品,还用于生产有机氯化物,如氯乙酸、环氧氯丙烷、一氯代苯等。也用于生产氯丁橡胶、塑料及增塑剂。日用化学工业用于生产合成洗涤剂原料烷基磺酸钠和烷基苯磺酸钠等。
The chemical industry is used in the production of inorganic chemical products such as sodium hypochlorite, aluminium trichloride, iron trichloride, bleaching, bromine and phosphorus. It is also used in the production of chlorinated rubber, plastics and plastics. The chemical industry is used in the production of sodium alkyl sulfonic acid and sodium alkyl sulfonic acid for synthetic detergents.
制环氧丙烷
of of chloropropane
在氯醇法生产环氧丙烷的过程中,有一步反应是丙烯与次氯酸反应生成氯醇,因此可将氯水用于氯醇化反应中,同时氯水可部分代替生产所用工艺水。
In the production of epoxypropane by chlorool, a step-by-step response is that acrylic and hypochloric acid react to the generation of chlorool, so that chlorowater can be used in the chloroethanol response, while chlorowater may partially replace the process water used for production.
反应方程式如下:
The response equation is as follows:
Cl2+H2O==HCIO+HCl;
CH3CHCH2+HCIO==CH3CHClCH2OH。
CH3CHClCH2OH+Ca(OH)2==CH3CHCH2O+CaCl2+2H2O。
制备氯化铁
Iron chloride
此方法利用工业盐酸或酸洗废液与废铁屑反应,生成氯化亚铁溶液,氯化亚铁溶液与废铁屑组成的循环吸收液与氯气发生氧化还原反应,氯气将Fe2+氧化为Fe3+,Fe3+被吸收液中的铁屑还原为Fe2+,Fe2+继续与氯气反应,形成循环吸收。
This method uses industrial hydrochloric acid or acid-washing liquids to react with scrap iron to produce a chlorinated sub-iron solution, a chlorinated sub-iron solution to oxidize the cycling solution with scrap iron scrap to regenerate the chlorine gas to Fe2+oxidize to Fe3+, Fe3+ to return to Fe2+, and Fe2+ to continue to react with chlorine to generate cycling.
涉及应方程式有:
The following equations are involved:
Fe+2H+=Fe2++H2↑;
2Fe2++Cl2=2Fe3++2Cl-;
2Fe3++Fe=3Fe2+。
制盐酸
hydrochloric acid
工业上制取盐酸时,首先在反应器中将氢气点燃,然后通入氯气进行反应,制得氯化氢气体,反应方程式为:H2+Cl2=2HCl。氯化氢气体冷却后被水吸收成为盐酸。在氯气和氢气的反应过程中,有毒的氯气被过量的氢气所包围,使氯气得到充分反应,防止了对空气的污染。
When industrial hydrochloric acid is produced, first the hydrogen gas is ignited in the reactor and then injected into the chlorine gas for reaction, producing the hydrogen chloride gas with the equation H2+Cl2=2HCl. The chlorinated hydrogen gas cools and is absorbed into the water as hydrochloric acid. During the reaction of the chlorine gas and hydrogen gas, the toxic chlorine gas is surrounded by excess hydrogen gas, allowing the chlorine gas to react adequately and preventing pollution of the air.
制聚氯乙烯
polyvinyl chloride
重单体制法可分为两种路线,一种是以乙烯为原料的石油路线,即氧氯化法。由石油裂解分离出乙烯,然后用氧气和HCl(裂解副产物)作用生成的Cl2与乙烯发生氯化反应,生成二氯乙烷,再裂解出氯化氢得氯乙烯。
The heavy monolithic system can be divided into two routes, the oil route based on ethylene, i.e., oxygen chloride. The Cl2 from the oil fission that separates ethylene and then reacts to ethylene chloride by oxygen and HCl (fibration by-product), producing ethylene dichloroethane and then dispersing ethylene chloride chloride.
其总反应方程式为:
Its overall response equation is:
4CH2=CH2+O2+2Cl2→4CH2=CHCl+2H2O
另一种为乙炔电石法。以电石为原料制备乙炔,然后与氯化氢反应制得氯乙烯。
The other is the acetylene electrostone. Acetylene is used as a raw material and then reacts to hydrogen chloride.
反应方程式为:
Response equations are:
CaC2+2H2O→4CHCH+Ca(OH)2;
CHCH+HCl→CH2=CHCl(反应条件为 HgCl2/C 120-180℃)。
CHCH+HClCH2=CHCl (reaction condition HgCl2/C 120-180°C).
制漂白物
bleach
氯气制成的漂白物很多,一般生活中涉及两种,NaClO和Ca(ClO)?。一般来说,消毒液是NaClO,一般用氯气通入氢氧化钠中制得。但其价格较高,工业漂白不用,常见于84。消毒粉则是Ca(ClO)?,因为其不够稳定一般为固体,是氯气通入石灰乳中制得,价格低廉,用于工业漂白,使用方法是加水溶解有效成分是次氯酸钙,从而漂白。保存以上漂白剂时,注意密封干燥,避免阳光直射。因为次氯酸盐在空气中会与二氧化碳、水发生反应,产生次氯酸,次氯酸在光照下分解,从而导致漂白剂失效。
In general, the disinfectant is NaCLO, which is produced with chlorine gas, and is produced with sodium hydroxide. But it is more expensive and industrial bleach is not used, usually 84. Disinfection powder is Ca (CLO)? Because it is not stable and generally solid, chlorine is produced in lime milk and is cheaply used for industrial bleaching by adding water soluble calcium hypochloride, so bleaching is used. When preserving the above bleaching agent, care is taken to seal it dry and avoid direct sunlight. Because it reacts with carbon dioxide, water, subchlorates are produced in the air, subchlorates are decomposed in photoluminous milk, and the subchloric acid is rendered ineffective.
制备次氯酸钙固体,用氢氧化钠溶液吸收含氯尾气得到的产物是次 氯酸钠溶液,得不到固体产物,不容易长时间保存。 用氢氧化钠和氢氧化钙的混合水溶液吸收氯气时, 能够得到次氯酸钙固体,便于储存和使用。
Calcium hypochlorite solids are prepared, and the product of chlorine tailings absorbed in sodium hydroxide solutions is the sodium chloride solution, which is not available for solid products and is not easily preserved for long. When chlorine gases are absorbed in mixed water solutions of sodium hydroxide and calcium hydroxide, calcium hypochloride solids are available for storage and use.
在电子工业中,高纯氯气主要用于电子工业干刻、光导纤维、晶体生长和热氧化。
In the electronics industry, high-purity chlorine gas is used mainly for dry carving, optical fibres, crystal growth and thermal oxidation in the electronics industry.
干法蚀刻
Dry etching
干法刻蚀是用等离子体进行薄膜刻蚀的技术。
Dry etching is the technique of membrane etching with plasma.
干刻又叫干法蚀刻,是指气固反应,气相产物主要有GaCl2,AsCl2和氢气,使用氯气做等离子蚀刻时,通常采用5%的高纯氯气+95%的氦气。
Dry carving, also known as dry etching, refers to the solid gas reaction, where gas phase products consist mainly of GaCl2, AsCl2 and hydrogen, and where chlorine gas is used for plasma etching, 5% of the high pure chlorine gas + 95% helium gas is usually used.
用氯气氧化降解制备纳米微晶纤维素
Preparation of nano-crystal cellulose from chlorine oxidation
中国专利公开了用氯气氧化降解制备纳米微晶纤维素的方法,与水解法制备纳米微晶纤维素相比,氯气氧化降解法利用了氯气水解所产生的次氯酸钠的漂白作用,可以使制得的纳米微晶纤维素光亮、洁白。
China's patents have made public the method of preparing nanocrystal cellulose using chlorine oxidation degradation, which uses bleaching of sodium hypochlorite from the hydrolysis of chlorine gas, compared to nanocrystal cellulose under hydrolysis, to make manufactured nanocrystal cellulose bright and white.
氯气还用于大规模集成电路、光纤、高温超导等技术领域。
Chlorine gas is also used in such technical areas as large-scale integrated circuits, fibre-optics, high-temperature superconductors, etc.
用于啤酒厂的污水处理
Sewage treatment for beer factories
中国专利公布了用氯气对啤酒厂污水进行处理的方法。氯气价格低廉,用量少,消毒可靠,工艺成熟,是自来水公司普遍使用的消毒剂,氯气还可以除臭、除微生物,对生物耗氧量和化学耗氧量去除率也很高,可确保回收水质的稳定,因而比较适合啤酒厂污水的处理。
Chinese patents publish methods for treating sewage from beer plants with chlorine gas. Chlorine gas is cheap, low in use, reliable in disinfection, mature in process, a disinfectant commonly used by running water companies. Chlorine gas can also deodorize, remove microorganisms, and remove high rates of bio- and chemical oxygen consumption, thus ensuring a stable recovery of water quality and thus is more suitable for treatment of sewage from beer plants.
自来水消毒
Water disinfection
自来水常用氯气消毒,1L水里约通入0.002g氯气,消毒原理是其与水反应生成了次氯酸,它的强氧化性能杀死水里的病菌。而之所以不直接用次氯酸为自来水杀菌消毒,是因为次氯酸易分解难保存、成本高、毒性较大,则用氯气消毒可使水中次氯酸的溶解、分解、合成达到平衡,浓度适宜,水中残余毒性较少。
The sterilized chlorine gas is commonly used in running water, while the 1L water in Rio enters 0.002 g chlorine gas. The disinfection principle is that it reacts to water by producing hypochloric acid, whose strong oxidation can kill germs in the water. The reason why subchloric acid is not used directly for sterilizing water is because it is difficult to preserve, costly and toxic, and the chlorine gas is used to disassemble, decomposition, and synthesizing in the water in a balanced manner, with appropriate concentrations and less residual toxicity in the water.
去除乙炔中的硫、磷杂质
Removal of parathion, phosphorus impurities in acetylene
乙炔气是PVC生产的主要原料。工业乙炔气中,硫、磷是以H2S和H3P气体形式存在的,这2种气体超标,会使生产PVC所用的催化剂中毒。利用氯水中的CIO-的强氧化性,对乙炔气进行喷淋洗涤,可除去H2S和H3P。
Acetylene gas is the main feedstock for PVC production. In the industrial acetylene gas, parathion, phosphorus are present in the form of H2S and H3P gases, which are overvalued and poisoning the catalysts used in the production of PVC. Using the strong oxidation of CIO- in chlorine water, the acetylene gas can be spray-washed to remove H2S and H3P.
反应方程式如下:
The response equation is as follows:
4ClO-+H2S→H2SO4+4Cl-
4ClO-+H3P→H3PO4+4Cl-。
农药工业用作生产高效杀虫剂、杀菌剂、除草剂、植物生长刺激剂的原料。
The pesticide industry is used as a feedstock for the production of highly efficient insecticides, microbicides, herbicides, plant growth irritants.
冶金工业主要用于生产金属钛、镁等。
Metallurgical Gold > b> Industrial is used mainly for the production of titanium, magnesium, etc.
人对不同浓度氯气的反应
human response to chlorine at different concentrations
| 浓度(mg/m3)(ppm) | 反应 |
| 30000(10000) | 一般滤过性防毒面具也无保护作用 |
| 3000(1000) | 深吸入少许可能危及生命 |
| 300(100) | 可能造成致命性伤害 |
| 120-180(40-60) | 接触30-60min可能引起严重损害 |
| 90(30) | 引起剧烈咳嗽 |
| 18(6) | 刺激咽喉 |
| 3-9(1-3) | 有明显的气味、刺激眼、鼻 |
| 1.5(0.5) | 略有气味 |
| 0.06(0.02) | 嗅觉不到浓度 |
急性毒性
Acute toxicity
实验动物急性中毒的表现最初是不安静,后呈衰弱、咳嗽、流泪、喷嚏、鼻腔分泌物增多等。吸入高浓度时可引起呼吸暂停;或先伴有气急,次为呼吸变慢、体温降低、血压降低,而导致肺水肿、血液浓缩等。并可见支气管扩张和间质性肺炎。
The acute intoxication of experimental animals was initially unsatisfied, followed by weakness, coughing, tears, sneezing, increased nasal secretion, etc.
慢性毒性
Chronic toxicity
实验动物慢性中毒大多体重减轻,抵抗力减弱,易感染呼吸道与肺部疾病。
Chronic toxicity in experimental animals is mostly reduced in body weight and resistance and prone to respiratory and pulmonary diseases.
“三致”作用与遗传毒性
Triple effect and genotoxicity
动物实验表明,氯气无致畸、致突变和致癌作用,也非促癌因素。
Animal experiments have shown that chlorine gas is not malformation, mutagenic and carcinogenic, nor is it a carcinogen.
中毒机理:
Poisoning mechanisms:
氯气是一种有毒气体,它主要通过呼吸道侵入人体并溶解在黏膜所含的水分里,生成次氯酸和盐酸,对上呼吸道黏膜造成损伤:次氯酸使组织受到强烈的氧化;盐酸刺激黏膜发生炎性肿胀,使呼吸道黏膜浮肿,大量分泌黏液,造成呼吸困难,所以氯气中毒的明显症状是发生剧烈的咳嗽。症状重时,会发生肺水肿,使循环作用困难而致死亡。由食道进入人体的氯气会使人恶心、呕吐、胸口疼痛和腹泻。1L空气中最多可允许含氯气0.001mg,超过这个量就会引起人体中毒。
Chlorine gas is a toxic gas that produces hypochloric acid and hydrochloric acid, causing damage to the upper respiratory mucous membrane, mainly through respiratory intrusion into the human body and solution in the water contained in the mucous membrane: hypochloric acid induces strong tissue oxidation; hydrochloric acid stimulates an inflammation of the mucous membranes, causing a high degree of secretion of viscous fluids and causing respiratory difficulties, so the obvious symptoms of chlorine gas poisoning are severe coughs. When symptoms are severe, pulmonary edema causes circulatory death. The chlorine gas entering the human body from the diet causes nausea, vomiting, chest pain and diarrhoea.
氯气吸入后与粘膜和呼吸道的水作用形成氯化氢和新生态氧。氯化氢可使上呼吸道粘膜炎性水肿、充血和坏死; 新生态氧对组织具有强烈的氧化作用,并可形成具细胞原浆毒作用的臭氧。氯浓度过高或接触时间较久,常可致深部呼吸道病变,使细支气管及肺泡受损,发生细支气管炎、肺炎及中毒性肺水肿。由于刺激作用使局部平滑肌痉挛而加剧通气障碍,加重缺氧状态; 高浓度氯吸入后,还可刺激迷走神经引起反射性的心跳停止。氯气中毒不可以进行人工呼吸。
Inhaled chlorine creates hydrogen chloride and new ecooxyoxygens with water in viscous membrane and respiratory tracts. Hydrochloride can cause inflammation of the upper respiratory respiratory membrane, blood-filling and death; New ecooxygens have a strong oxidation effect on tissues and can form ozone with cell-based pulp toxicity. High concentrations of chlorine or prolonged exposure can cause deep respiratory aberrations that cause damage to the bronchial tubes and lung blisters, minor bronchitis, pneumonia, and middle-toxic pulmonary edema. As a result of the stimuli, local smoothing muscle spasms, they exacerbate the lack of oxygen; High concentrations of chlorine can also stimulate neurism leading to a reactionary cardiac arrest. Chloric poisoning does not allow for artificial respiration.
临床表现
Clinical performance
急性中毒主要为呼吸系统损害的表现。
Acute poisoning is mainly a manifestation of respiratory damage.
a、 起病及病情变化一般均较迅速。
a. Morbidity and changes in conditions are generally relatively rapid.
b、 可发生咽喉炎、支气管炎、肺炎或肺水肿,表现为咽痛、呛咳、咳少量痰、气急、胸闷或咳粉红色泡沫痰、呼吸困难等症状,肺部可无明显阳性体征或有干、湿性罗音。有时伴有恶心、呕吐等症状。
b. Pneumonia, bronchitis, pneumonia or emphysema can occur in the form of osteoporosis, cough, cough, coughing, ache, chest or coughing of pink foams, breathing difficulties, etc., with no visible positive signs or dry, wet dysentery in the lungs.
c、 重症者尚可出现急性呼吸窘迫综合征,有进行性呼吸频速和窘迫、心动过速,顽固性低氧血症,用一般氧疗无效。
c. Acute respiratory distress syndrome can still be observed for persons with severe illnesses, with sexual respiratory frequency and distress, heart excesses, obstinate hypoxia and general aerobic therapy ineffective.
d、 少数患者有哮喘样发作,出现喘息,肺部有哮喘音。
d. A small number of patients suffer from asthma, asthma and asthma in their lungs.
e、 极高浓度时可引起声门痉挛或水肿、支气管痉挛或反射性呼吸中枢抑制而致迅速窒息死亡。
e. Rapid suffocation to death at very high concentrations, resulting in spasm or oedema, bronchial convulsions or reflective respiratory central inhibition.
f、 病发症主要有肺部继发感染、心肌损害及气胸、纵隔气肿等。
(f) The main causes of the disease are pulmonary infections, myocardial damage and air chests, bloated blobs, etc.
g、 X线检查:可无异常,或有两侧肺纹理增强、点状或片状边界模糊阴影或云雾状、蝶翼状阴影。
g. X-ray examination: No abnormality, or pneumonic reinforcements on both sides of the lung, blurring shadows of the point or fragmentary boundary or cloudy clouds, wings-like shadows.
h、 血气分析:病情较重者动脉血氧分压明显降低。
h. Gas analysis: there has been a significant reduction in the blood oxidation of the arteries of persons with higher levels of illness.
i、心电图检查:中毒后由于缺氧、肺动脉高压以及植物神经功能障碍等,可导致心肌损害及心律失常。
i. EKG: Aerobic intoxication, pulmonary pulmonary hypertension and phyto-neurological disorders can lead to heart muscle damage and cardiac arrhythmia.
眼损害:氯可引起急性结膜炎,高浓度氯气或液氯可引起眼灼伤。
Eye damage: Chlorine can cause acute membrane and high concentrations of chlorine gas or liquid chlorine can cause eye burns.
皮肤损害:液氯或高浓度氯气可引起皮肤暴露部位急性皮炎或灼伤。
Skin damage: A liquid chlorine or a high chlorine concentration can cause acute skin inflammation or burns in the skin exposure.
中毒处理
Treatment of poisoning
吸入气体者立即脱离现场至空气新鲜处,保持安静及保暖。眼或皮肤接触液氯时立即用清水彻底冲洗。
The person who inhales the gas immediately leaves the site for fresh air and remains quiet and warms it.
吸入后有症状者至少观察12小时,对症处理。吸入量较多者应卧床休息,吸氧,给舒喘灵气雾剂、喘乐宁(Ventolin)或5%碳酸氢钠加地塞米松等雾化吸入。
Inhaled symptoms are observed for at least 12 hours and treated. Those with greater inhalation should rest in bed, take oxygen, and breathe mists, such as salbutamol aerosols, Ventolin or 5% sodium carbonate plus sermion.
其他对症处理。
Other treatments.
泄露处理
Leakage Treatment
氯气发生泄漏后,应采取针对性的应急措施。泄漏污染区人员应迅速撤离至上(侧)风处,并立即设置警戒,小泄漏时,于150米处设置警戒,大泄漏时,于450米设置警戒。消防人员必须佩戴空气呼吸器或氧气呼吸器,穿全身防火防毒服,手戴橡胶手套,在上风向进行处置。尽可能切断泄漏源,合理通风,加速扩散,喷雾状水稀释、溶解,构筑围堤或挖坑收容产生的大量废水。如有可能,用管道将泄漏物导至还原剂(酸式硫酸钠或酸式碳酸钠)溶液中或将漏气钢瓶浸入石灰乳液中。具体处置措施为:
Firefighters must wear air respirators or oxygen respirators, wear all-round fireproofs, wear rubber gloves, and dispose of them in the upper wind direction. If possible, the source should be cut off, properly ventilated, accelerated dispersion, spray water dilution, disassembly, embankment or digging pits to absorb large amounts of wastewater.
(一)关阀断源。生产装置发生氯气泄漏,事故单位的工程技术人员或熟悉工艺的人员关闭输送物料的管道阀门,断绝物料供应,切断事故源,公安消防队出开花或喷雾水枪掩护并协助操作。
(i) Shut down the source of the valve. There was a chlorine leak in the production unit, the engineering technicians of the accident unit or persons familiar with the process shut down the pipeline valves for the delivery of the material, cut off the supply of the material, cut off the source of the accident, and the Public Safety Fire Brigade provided cover for the opening of flowers or spray water guns and assisted in the operation.
(二)倒罐转移。储罐、容器壁发生泄漏,无法堵漏时,可采用疏导的方法将液氯倒入其他容器或储罐。
(ii) Repository transfer. If there is a leak in the tank or container wall and it cannot be blocked, the liquid chlorine may be poured into other containers or tanks by channeling.
(三)化学中和。储罐、容器壁发生少量泄漏,可采用化学中和的方法,即在消防车水罐中加入生石灰、苏打粉等碱性物质,向罐体、容器喷射,以减轻危害,也可将泄漏的液氯导至碳酸钠溶液中,使其中和,形成无危害或微毒废水。具体反应为CaO+H2O一Ca(OH)2,2Ca(OH)2+2Cl2一CaCl2+Ca(CIO)2+2H2O。生成氯化钙和次氯酸钙,都没有毒害作用。如果现场温度比较高,则生成氯化钙和氯酸钙。产物的沉降度比较好,不会形成悬浮物,很快降落到地面,对地面植物起到钙肥作用。
(iii) Chemically neutralized. Small leaks from storage tanks and container walls can be performed by means of chemical neutralization, i.e. the insertion of alkaline substances, such as lime and soda powder, into water tanks of fire-fighting vehicles, to spray into tanks and containers in order to mitigate the hazards, or by directing leaking liquid chlorine to sodium carbonate solutions, resulting in the formation of non-hazardous or very toxic wastewater. This is reflected in Cao+H2O1Ca (OH)2,2Ca (OH)2Cl2ICl2+Ca (CIO)2+2H2O. The generation of calcium chloride and calcium subchlorate is toxic. If the temperature is higher in the field, it produces calcium chloride and calcium chloride products with a better degree of deposition and does not create a suspended substance, which quickly lands on the ground and produces calcium fertilization for plants on the ground.
(四)稀释降毒。以泄漏点为中心,在储罐、容器壁的四周设置水幕或喷雾水枪喷射雾状水进行稀释降毒,但不宜使用直流水或直接对准泄漏点喷射,避免氯气与水作用生成酸,加速对泄漏点的腐蚀。除了使氯气溶解于水外,还可以利用氯气与水的反应加大对空气中氯气的吸收。
(iv) Diagnosis. A water curtain or spray-gun spray-like water around a storage tank or container wall is placed at the centre of the leak point to dilute the precipitation, but it is not appropriate to use direct flow water or direct injection to the spill point to avoid the production of acid by chlorine gas and water and to accelerate the corrosion of the leak point. In addition to soluting the chlorine gas into water, the chlorine-water reaction may be used to increase the absorption of the chlorine gas in the air.
(五)浸泡水解。运输途中体积较小的液氯钢瓶阀门损坏,发生泄漏,又无堵漏器具无法制止外泄时,可将钢瓶浸入氢氧化钙等碱性溶液中进行中和,也可将钢瓶浸入水中。
(v) Pulse hydrolysis. When a smaller liquid chlorine steel bottle valve is damaged during transport, leaks occur and no leaking device is unable to stop the release, the steel bottle may be immersed in alkaline solution, such as calcium hydroxide, or the steel bottle may be immersed in water.
(六)器具堵漏。管道壁发生泄漏,且泄漏点处在阀门以前或阀门损坏,不能够关阀止漏时,可使用不同形状的堵漏垫、堵漏楔、堵漏袋等器具实施封堵。(a)微孔跑冒滴漏可用螺丝钉加粘合剂旋入孔内的方法堵漏。(b)罐壁撕裂发生泄漏,可用充气袋、充气垫等专用器具从外部包裹堵漏。(c)带压管道泄漏,可用捆绑式充气堵漏带或使用金属外壳内衬橡胶垫等专用器具实施内外堵漏。(d)阀门法兰盘或法兰垫片损坏,发生泄漏,可用不同型号的法兰夹具,并注射密封胶的方法进行封堵,也可直接使用专门的阀门堵漏工具实施堵漏。
(vi) Device leaks. If leaks occur, the leaking point is damaged before the valves or the valves are not able to close the valves and the leaks can be closed by means of devices of different shapes, such as leak pads, leaks, leak bags, etc. (a) microholes run through leaks by means of screws and glues that can flow into the hole. (b) leaks occur when leaks occur, special devices, such as gas bags, gas cushions, etc., can leak from external packages. (c) leaks can be used for internal and external leaks by means of special devices, such as bundle-filled gas belts or rubber cushions in metal casings. (d) broken valves or flang mats are damaged, leaks occur, can be covered by different types of flanges and can be injected with seals, or leaks can be implemented directly by means of special valves.
(七)洗消处理。一是化学消毒法。即用氢氧化钠、氨水、碳酸氢钠等碱性物质溶于水中,喷洒在污染区域或受污染体表面,发生化学反应改变毒物性质,成为无毒或低毒物质;二是物理消毒。即用吸附垫、活性炭等具有吸附能力的物质,吸附回收后转移处理;对染毒空气可用水驱动排烟机吹散降毒,也可对污染区暂时封闭,依靠自然条件如日晒、通风使毒气消失;也可喷射雾状水进行稀释降毒。
(vii) Disinfection. First, chemical disinfection. Alkaline substances such as sodium hydroxide, ammonia, sodium carbonate are soluble in water, sprayed in contaminated areas or on the surface of the contaminated body, chemically reacting to change the venomic properties and become non-toxic or low-toxic substances; second, physical disinfection. This is the transfer of sorbentary substances such as sorbent pads, activated carbon, etc., by sorbenting and subsequent recovery treatment; water-driven smokers can be blown and detoxified; contaminated areas can also be temporarily closed, depending on natural conditions, such as sunlight, ventilation, which can cause the gas to disappear; and spray fog water can also be diluted and detoxified.
储运过程中爆炸燃烧危险性
Explosive fire hazard during storage
由于物质急剧氧化或分解反应,使温度、压力增加或使两者同时增加的现象,称为爆炸。发生爆炸时,势能(化学能或者机械能)突然转变为动能,有高压气体生成或者释放出高压气体,这些高压气体随之做机械功,如移动、形状改变和抛射周围的物体。爆炸分为物理爆炸、化学爆炸和核爆炸,物理爆炸是由于液体变成蒸汽或气体迅速膨胀,压力急速增加,并大大超过容器的极限压力而发生的爆炸;化学爆炸是因物质本身起化学反应,产生大量的气体和高温而发生的爆炸。氯气生产储运过程中的爆炸兼有物理和化学爆炸两种可能。
As a result of the rapid oxidation or decomposition of the substance, the temperature, pressure increase or increase both are referred to as explosions. When an explosion occurs, the energy (chemical or mechanical) suddenly transforms into kinetic energy, with high pressure gases generating or releasing high pressure gases, which then do mechanical work, such as moving, changing shapes and ejecting around objects. The explosion is divided into physical explosions, chemical explosions, and nuclear explosions, which occur as a result of the rapid expansion of liquids into vapours or gases, rapidly increasing pressure and significantly exceeding the maximum pressure of the container; the chemical explosion is an explosion that occurs as a result of the chemical reaction of the substance itself, producing large quantities of gases and high temperatures.
 氯气泄漏处理液氯在生产和贮运中易发生下列问题:
氯气泄漏处理液氯在生产和贮运中易发生下列问题:
Chlorine Leakage Treatment
①液化尾气中氯气、氢气与空气的混合气爆炸;
1 mixed gas explosion of chlorine, hydrogen and air in liquefied tail gas;
②包装容器中残存有机物杂质与氯气反应爆炸;
2 The residual organic impurities in packagings and the chlorine gas reaction explosion;
③水和食盐水溶液中铵盐带入液化系统,会使液氯中三氯化氮积累而引起爆炸。
The introduction of ammonium salt into the liquefied system in water and salt-eating water solutions can cause the accumulation of trichloride nitrogen in liquid chlorine to explode.
当液氯蒸发用完后,所用容器均须用水和碱水冲洗,以除去被三氯化氮污染的液氯后,方能修理和使用。氯是剧毒物,生产中对受压容器等设备应严格要求,防止氯气泄漏。空气中氯气允许浓度不大于1ppm。
When liquid chlorine is evaporated, the containers used must be rinsed with water and alkali water to remove the liquid chlorine contaminated with nitrogen trichloride before it can be repaired and used. Chlorine is highly toxic and equipment such as pressurized containers should be strictly required in production to prevent leakage of chlorine gas. The permitted concentration of chlorine gas in air is not greater than 1 ppm.
氯气液化
Liquidation of chlorine gas
氯气通常可直接利用,但为了制取纯净的氯气,并考虑贮运的方便,而把一部分氯气进行液化制成液氯,用钢瓶或槽车运往用户。生产中,将从电解槽出来的热氯气(其中含有少量氢、氧和二氧化碳等杂质),用冷水洗涤或在换热器内冷凝脱水,再用硫酸干燥(必要时可以液氯洗涤以除去水分和杂质),然后送去液化。因湿氯对铁有腐蚀作用,液化前氯中水分应低于50ppm。
Chlorine gas is usually used directly, but in order to produce pure chlorine gas and to take into account the convenience of storage, a portion of chlorine gas is liquefied into liquid chlorine and transported to users in steel bottles or tanks. In production, the thermal chlorine gas from electrolysis tanks (which contains a small amount of impurities such as hydrogen, oxygen and carbon dioxide) is washed in cold water or condensed in heat exchange units, dried with sulphuric acid (where necessary, liquid chlorine can be scrubbed to remove moisture and impurities) and sent to liquefied. As wet chlorine has corrosive effects on iron, the water fraction in pre-liquid chlorine should be less than 50 ppm.
 液氯钢瓶氯气液化的常用方法有:(1)低温法;(2)直接压缩法或高压法;(3)低温压缩法或综合法。
液氯钢瓶氯气液化的常用方法有:(1)低温法;(2)直接压缩法或高压法;(3)低温压缩法或综合法。
氯气液化的温度和压力范围很大,工业生产上分为低压法、中压法和高压法。低压法在氯气为0.078~0.147MPa(表压),冷却温度为-35~-40℃下进行液化。中压法在氯气为0.245~0.49MPa,冷却温度为-15~-20℃下进行液化。高压法的氯气为0.98~1.17MPa,用15~25℃水冷却即可液化。高压法比低压法能耗低,循环水用量少,但设备费用较高,适于大规模生产使用,中、小型氯碱厂多采用中压法。液化率由氯中含氢量来决定。液化尾气中含氢不得超过4%(体积)。尾气含60%~70%的氯气可作为合成盐酸、氯苯、次氯酸盐的原料气,也可经过深度净化精制,使液化率达到98%~99%。
The temperature and pressure range of chlorine gas liquefied is large, and industrial production is divided into low-pressure, medium-pressure and high-pressure methods. The low-pressure method is 0.078 - 0.147 MPa (ceremonial pressure) for chlorine gas, with a cooling temperature of -35 - 40°C. The medium-pressure method is 0.245 - 0.49 MPa for chlorine gas, with a cooling temperature of not more than 15 - 20°C. The high-pressure chlorine method is 0.98 - 1.17 MPa, with 15 - 25°C water cooling and can be liquefied. The high-pressure method is lower than the low-pressure method, with less recycling water use, but the equipment is more expensive for large-scale production and medium-pressure is more likely to be used in small- and medium-scale chlor-alkali plants.
氯气泄漏极易造成人身伤亡和区域性污染,防止氯气泄漏的方法有:
Chlorine leaks are highly vulnerable to human casualties and regional pollution, and can be prevented by:
①不能选用存在缺陷的设备和部件,各设备和部件要定期检测和检验;
1 Equipment and components that are defective cannot be selected and are subject to periodic testing and inspection;
②加强工艺管理,严格控制工艺指标,发现问题必须及时检查和处理;
Strengthen process management, strictly control process indicators and detect problems that must be inspected and addressed in a timely manner;
③加强事故氯处理装置的管理和检修,相关装置采用多路电源供电,定期清洗事故氯处理装置,机泵定期试车;
3. Strengthen the management and repair of accident chlorine treatment units, which are supplied with multiple circuit power, regularly clean up accident chlorine treatment units, and regularly test vehicles with pumps;
④为了及时发现氯气泄漏,在生产、储存、输送和使用的岗位都要安装氯气报警器,一旦氯气泄漏,可及早发现,防止事故扩大,并在液化岗位安装电视监控和碱液喷淋装置;
In order to detect chlorine gas leaks in a timely manner, chlorine gas alarms should be installed in production, storage, transmission and use positions, early detection in case of chlorine leaks, prevention of accidents and installation of television surveillance and alkaline spraying units in liquefied positions;
⑤加强对职工的安全教育和培训。
Strengthen safety education and training for employees.
职业卫生标准:中国MAC 1 mg/m3;美国ACGIH TLV-STEL 2.9 mg/m3 (1 ppm); TLV-TWA 1.5 mg/m3 (0.5 ppm)
Occupational health standards: MAC 1 mg/m3 in China; ACGIH TLV-STEL 2.9 mg/m3 (1 ppm); TLV-TWA 1.5 mg/m3 (0.5 ppm)
中国职业病诊断国家标准:职业性急性氯气中毒诊断标准及处理原则GB4866-1996。
China National Criteria for Diagnosis of Occupational Diseases: Criteria for Diagnosis of Occupational Acute Chlorine Poisoning and Principles for Treatment GB4866-1996.
危规:GB2.3类23002(液化的)。原铁规:剧毒气体,31001.UN NO.1017。IMDG CODE 2028页,2类。副危险6.1。
Catastrophes: GB2.3 Class 2302 (Liquefied). Code iron: highly toxic gases, 3101.UN No. 1017. IMDG CODE 2028, Category 2. Sub-hazard 6.1.
2004年4月15日傍晚19时,重庆天原化工厂由于氯罐及相关设备陈旧发生氯气泄漏事件,导致排污罐发生爆炸;4月16日下午5时57分,重庆天原化工厂有关人员在处置氯气泄漏事故时违规操作,导致液氯贮气罐发生爆炸。事故造成9人死亡,3人受伤,15万群众被疏散。
On the evening of 15 April 2004, at 1900 hours, as a result of a chlorine leak at the Chongqing plant and related equipment, the sewage tank exploded; on 16 April, at 5.57 p.m., the personnel at Chongqing chemical plant acted in an irregular manner in dealing with the chlorine gas leak, resulting in an explosion of the liquid chlorine tank. Nine people were killed, three were injured and 150,000 were evacuated.
2016年4月12日17时许,山西省临猗县一废品收购站发生氯气泄漏事件,附近一所小学的数十名小学生随后出现呼吸不适和腹部疼痛症状,被送往临猗县人民医院接受治疗。
On 12 April 2016, at about 1700 hours, a chlorine gas leak occurred at a scrap buying station in Pingjong County, Shanxi Province, and dozens of primary schoolchildren in a nearby primary school subsequently showed signs of respiratory and abdominal pain and were taken to the Pingjong District People's Hospital for medical treatment.
自2002年5月起,我省消防部队己经成功处置氯气泄漏及泄漏引起火灾事故共二十余起。2002年5月28日黄石市矿务局金昌公司的氯气泄漏,消防部队成功处置并疏散2000余户居民,约6400多人;2003年11月6日武汉市桥口区简易街东风造纸厂氯气储罐(容量1吨)发生泄漏,消防部队从现场救出200余人,成功堵漏并安全转移储罐。
Since May 2002, my provincial fire service has successfully disposed of chlorine gas leaks and fires caused by them. On 28 May 2002, the gold-chang company of the Yellowstone mining authority successfully disposed of and evacuated more than 2,000 households, more than 6,400 people; and on 6 November 2003, there was a leak in the chlorine storage tank (one ton) at the Far East Paper Factory in Wuhan Bridge District, where the fire brigade rescued more than 200 people from the site and successfully blocked and safely transferred the storage tanks.
注册有任何问题请添加 微信:MVIP619 拉你进入群

打开微信扫一扫
添加客服
进入交流群















发表评论